Categories
- Aircraft, Helicopter, UAV, Spacecraft & related equipment
- Services (R&D, training, engineering, consultancy, …)
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), is a national space agency and specializes in developing technologies related to the Space sector including Satellites, Launch vehicles, Sounding Rockets and Associated ground systems.
History
India decided to go to space when Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was set up by the Government of India in 1962. With the visionary Dr Vikram Sarabhai at its helm, INCOSPAR set up the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Thiruvananthapuram for upper atmospheric research.
Indian Space Research Organisation, formed in 1969, superseded the erstwhile INCOSPAR. Vikram Sarabhai, having identified the role and importance of space technology in a Nation's development, provided ISRO the necessary direction to function as an agent of development. ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently.
Throughout the years, ISRO has upheld its mission of bringing space to the service of the common man, to the service of the Nation. In the process, it has become one of the six largest space agencies in the world. ISRO maintains one of the largest fleet of communication satellites (INSAT) and remote sensing (IRS) satellites, that cater to the ever growing demand for fast and reliable communication and earth observation respectively. ISRO develops and delivers application specific satellite products and tools to the Nation: broadcasts, communications, weather forecasts, disaster management tools, Geographic Information Systems, cartography, navigation, telemedicine, dedicated distance education satellites being some of them.
To achieve complete self reliance in terms of these applications, it was essential to develop cost efficient and reliable launch systems, which took shape in the form of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). The famed PSLV went on to become a favoured carrier for satellites of various countries due to its reliability and cost efficiency, promoting unprecedented international collaboration. The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) was developed keeping in mind the heavier and more demanding Geosynchronous communication satellites.
Apart from technological capability, ISRO has also contributed to science and science education in the country. Various dedicated research centres and autonomous institutions for remote sensing, astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences and space sciences in general function under the aegis of Department of Space. ISRO's own Lunar and interplanetary missions along with other scientific projects encourage and promote science education, apart from providing valuable data to the scientific community which in turn enriches science.
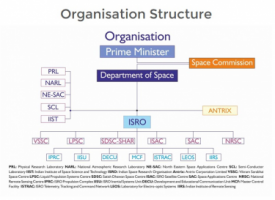
Centres
-
ISRO CentresVikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC),
-
Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC),
-
SDSC SHAR,
-
ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC),
-
IPRC Mahendragiri,
-
Space Applications Centre (SAC),
-
National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC),
-
ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC),
-
ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU),
-
Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems (LEOS),
-
Development and Educational Communication Unit (DECU),
-
Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST),
-
Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS),
-
Physical Research Laboratory (PRL),
-
National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL),
-
Master Control Facility (MCF),
-
North Eastern-Space Applications Centre (NE-SAC),
-
Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL),
-
Department of Space and ISRO HQ,
-
Antrix Corporation Limited.
Vision
The Organization's vision is to harness space technology for national development, while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.
Mission
The Organization's mission is to:
- Design and development of launch vehicles and related technologies for providing access to space.
- Design and development of satellites and related technologies for earth observation, communication, navigation, meteorology and space science.
- Indian National Satellite (INSAT) programme for meeting telecommunication, television broadcasting and developmental applications.
- Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) programme for management of natural resources and monitoring of environment using space based imagery.
- Space based Applications for Societal development and Disaster Management Support.
- Research and Development in space science and planetary exploration.
Objectives
The Organization's Objectives are:
-
Operational flights of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV),
-
Developmental flight of Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV- Mk II),
-
Development of heavy lift Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-Mk III),
-
Development of semi-cryogenic technology for future launch vehicles,
-
Design, Development and Realization of Communication Satellites,
-
Design, Development and Realization of Earth Observation Satellites,
-
Development of Navigation Satellite Systems,
-
Development of Space Science and Planetary Exploration Satellite Systems,
-
Earth Observation Applications,
-
Space based systems for Societal Applications,
-
Advanced Technologies and newer initiatives,
-
Training, Capacity building and Education,
-
Promotion of Space technology,
-
Infrastructure, Facility Development & Mission Operations Support,
-
International Cooperation.
Indian Space Research Organisation - ISRO
- Hqs: Antariksh Bhavan, New BEL Road, 560 231, Bangalore, India
- +91 80 2341 5275, +91 80 2217 2296
- +91 80 2341 2253
- dir.ppr@isro.gov.in
- www.isro.gov.in